You may be wondering what languages do they speak in Egypt? Is Egyptian a language?
The answer to that is complicated as today most people in Egypt speak a dialect of Arabic called Egyptian Arabic.
In addition, there’s also some people in Egypt who still use the old Ancient Egyptian language.
Table of Contents
Is Egyptian a Language?
Egyptian isn’t a language however Ancient Egyptian was a language spoken in ancient Egypt and it still exists today in the form of the Coptic language.
For over four thousand years, the people of Egypt spoke this Ancient Egyptian language until it was gradually replaced by Arabic after the Arab conquest of Egypt in the year 641.
The Ancient Egyptian language eventually evolved into the Coptic language which still exists in Egypt today but is mainly used during services by the Coptic Orthodox Church.
There are actually millions of people in Egypt who can still understand Coptic.
‘Egyptian’ is also commonly used to refer to Egyptian Arabic which is a dialect of Arabic that is spoken by the majority of people who live in Egypt today.
How Many Languages are Spoken in Egypt?
According to Ethnologue, there are 16 different languages spoken in Egypt today.
The official language of Egypt is Arabic and most Egyptians speak one of several Arabic dialects.
There are also several native languages, immigrant languages and other foreign languages that are commonly used in Egypt.
What Language is Spoken in Egypt?
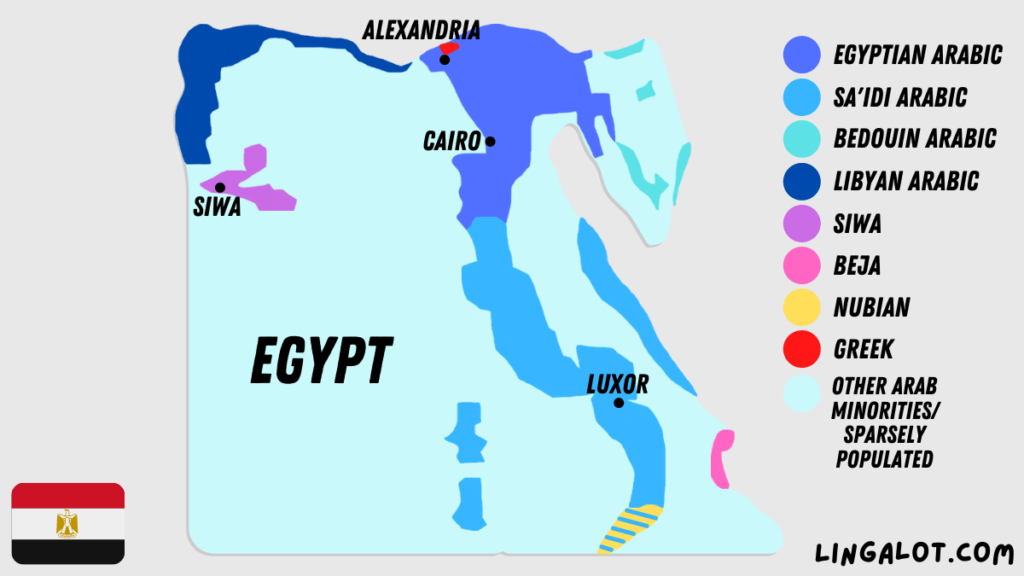
Approximately 99% of the population of Egypt speak a dialect of Arabic as their first language.
Whilst the official language of Egypt is actually Modern Standard Arabic, this version is mainly used in written documents and in schools.
The largest Arabic dialect spoken in Egypt is Egyptian Arabic which also serves as the lingua franca. Egyptian Arabic is spoken by 68% of people in Egypt.
Egyptian Arabic is a mix of Arabic, Coptic, Ottoman Turkish, French and Italian influences making it fairly unique.
The second largest Arabic dialect spoken in Egypt is Sa’idi Arabic which is spoken by 29% of the population.
In southern Egypt, Sa’idi Arabic is actually the main spoken language. This dialect of Arabic is mainly spoken near the Sudanese border by rural populations as well as along the Nile river.
Other Arabic dialects spoken in Egypt are:
- Bedouin Arabic – spoken by 1.6% of the population who mainly live in the Sinai Peninsula.
- Sudanese Arabic – spoken by 0.6% of the population who are mainly Sudanese immigrants.
- Eastern Libyan Arabic – spoken by 0.1% of the population who reside mainly in the western desert near Libya.
Other Languages Spoken In Egypt
In the Upper Nile Valley, there are around 300,000 speakers of Nubian languages, mainly Nobiin.
In the Eastern Desert and along the coast of the Red Sea, there are around 77,000 speakers of Beja.
Just north of Cairo, around 234,000 Dom people speak the Domari language.
In the Siwa oasis, around 30,000 Egyptian Berbers speak the Siwi Berber language.
There are also a number of immigrant languages that are commonly spoken in Egypt. These include Amharic, Greek, Armenian, Italian and Adyghe.
The most popular foreign languages in Egypt are English, French and Italian. Educated Egyptians tend to speak English and/or French as second languages.
Why Does Egypt Speak Arabic?
You may now be wondering ‘why does Egypt speak Arabic?’ and ‘what happened to the Ancient Egyptian language?’.
Arabic was first brought to Egypt during the Muslim conquest of Egypt which took place between the years 639 and 646.
This conquest ended the seven century long period of Roman rule that had begun in 30 BC.
The invasion began at the end of 639 when a force of 4,000 troops left for Egypt.
Most of the soldiers belonged to the Arab tribe of ‘Ak but one third of the soldiers belonged to the Arab tribe of Ghafik.
The invasion was completed by 646 and by then Egypt was completely under Arab rule.
Arabic was actually spoken in parts of Egypt before the arrival of Islam. This was mainly in the Eastern Desert and Sinai which were closer to the Arab speaking world.
Nile Valley Egyptians slowly adopted Arabic after the Muslim conquest. Prior to this, they spoke either Coptic (ancient Egyptian) or Koine Greek.
There was a period of Coptic/Arabic bilingualism which lasted for more than 3 centuries.
Is Arabic and Egyptian the Same Language?
Modern Standard Arabic and Egyptian Arabic are not the same as Egyptian Arabic is a dialect of Arabic.
A language is a structured form of communication whereas a dialect is just a regional version of a language.
Arabic is also very different to the Ancient Egyptian language that was spoken in Egypt before Muslim conquest.
The Egyptian Arabic dialect has a lot of Coptic influence with some Coptic words being used in the Egyptian dialect.
Note: Coptic is a version of the Ancient Egyptian language (more on this later).
For example, in Egyptian Arabic the word for ‘yes’ is aywa whereas in Standard Arabic, it is na’am. Aywa is actually derived from Coptic.
As the Egyptian Coptic language was the native language of the vast majority of Nile Valley Egyptians prior to Muslim conquest, the grammar structure and vocabulary of the Egyptian Arabic dialect has been hugely influenced by Coptic.
The dialect was then later influenced by other foreign and colonial languages including French, Italian, Greek, Ottoman Turkish and English.
Egyptian Arabic vs Standard Arabic
There are several major differences between Modern Standard Arabic and Egyptian Arabic.
They have different sentence structures, very different grammar and some differing pronunciation of letters and words.
There are some vocabulary differences, mainly words adopted from other languages like Coptic, but vocabulary is largely the same.
There are still many differences though such as:
How are you?
- In Egyptian Arabic, this phrase is ‘izzayak/izzayik?’.
- In Modern Standard Arabic, this phrase is ‘kayfa halok?’.
Something important to note is that Modern Standard Arabic isn’t a conversational language meaning you’ll never hear people on the street speaking it.
It’s only used in documents, books, newspapers and also on TV (usually the news).
Dialects of Arabic, including Egyptian Arabic, are spoken languages and are how people communicate with each other.
Egyptian Arabic Phrases
Below I’ve listed some common Egyptian Arabic words and phrases so you can see how the language looks and sounds.
- Hello (peace be upon you) – Salaam ‘aleikum سلام عليكم
- How are you? – Izzayak / Izzayik? ازيك؟
- Everything’s great – Kullu tamaamh كله تمام
- Thank you – Shokran شكرا
- My name is… – Esmee… …اسمي
- I am from… – Ana men… …انا من
- Ok – Maashi ماشى
- Congratulations! – Mabrook! !مبروك
As you can see from the phrases listed above, whilst Egyptian Arabic isn’t its own language, there are plenty of words and expressions that make Egyptian Arabic distinct.
What Language was Spoken in Ancient Egypt?

The Ancient Egyptian language was an Afro-Asiatic language that was spoken in ancient Egypt.
This language is closely related to the Berber and Semitic languages like Hebrew still spoken today.
The Ancient Egyptian language evolved over the years starting with Old Egyptian then Middle Egyptian then Late Egyptian then Demotic and then finally Coptic.
The use of the Egyptian language spans over a long period of time with Old Egyptian dating back to the mid-4th millennium BC in the Old Kingdom of Egypt.
The use of the later Coptic language eventually largely fell out of use by the 17th century but is still used in some communities today.
The 5 stages of the Egyptian language:
- Old Egyptian: spoken from 2600 – 2000 BC
- Middle Egyptian: spoken from 2000 – 1350 BC
- Late Egyptian: spoken from 1350 – 700 BC
- Demotic: 700 BC – 400 AD
- Coptic: 200 AD onwards
Ancient Egyptian Writing System
These 5 stages were actually written in 4 different scripts: hieroglyphs, hieratic, demotic and then coptic.
Famously, Ancient Egyptian was written in hieroglyphics which use various symbols that look like people, animals, objects and more.
The earliest texts using hieroglyphics date back to 3200 BC. The last hieroglyphic inscription was written in the 5th century AD (3500 years after the first).
Whilst the hieroglyphics were beautiful, they were time consuming to write so eventually other scripts were developed.
The ancient Egyptians invented the hieratic script which was a cursive form of hieroglyphics and this system of writing was used alongside hieroglyphics for most of Egyptian history.
Eventually the hieratic script was developed into the demotic and coptic scripts.
Ancient Egyptian Words
To give you a taste of the Ancient Egyptian language (as it was spoken back in days of ancient Egypt), I’ve listed some key words and phrases:
- In peace (common greeting) – em hotep
- Welcome – ii-wey
- Hello – ii-ti
- Thank you – dewa-netjer en-ek (when speaking to a male), dewa-netjer en-etj (when speaking to a female)
You should now be able to say a few simple words in the Ancient Egyptian language. Cool right!?
Thanks for reading this post on the languages spoken in Egypt which answers the question ‘is Egyptian a language?’.
Although Egyptian Arabic isn’t a language, it’s clear that the languages spoken in Egypt are distinct and have their own twist.
The culture and history of Egypt has influenced the languages spoken there today including influencing its own dialect of Arabic.
Related Posts:
